How to Draw Parse Tree for Given Grammer
Ambiguous Grammar & Parse Tree-
We have discussed-
- Ambiguous Grammar generates at least one string that has more than one parse tree.
- Parse Tree is the geometrical representation of a derivation.
In this article, we will discuss important points about Ambiguous Grammar and Parse Tree.
Important Points-
Point-01:
- There always exists a unique parse tree corresponding to each leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation.
If n parse trees exist for any string w, then there will be-
- n corresponding leftmost derivations.
- n corresponding rightmost derivations.
Point-02:
For ambiguous grammars,
- More than one leftmost derivation and more than one rightmost derivation exist for at least one string.
- Leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation represents different parse trees.
Point-03:
For unambiguous grammars,
- A unique leftmost derivation and a unique rightmost derivation exist for all the strings.
- Leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation represents the same parse tree.
Point-04:
- There may exist derivations for a string which are neither leftmost nor rightmost.
Example
Consider the following grammar-
S → ABC
A → a
B → b
C → c
Consider a string w = abc.
Total 6 derivations exist for string w.
The following 4 derivations are neither leftmost nor rightmost-
Derivation-01:
S → ABC
→ aBC (Using A → a)
→ aBc (Using C → c)
→ abc (Using B → b)
Derivation-02:
S → ABC
→ AbC (Using B → b)
→ abC (Using A → a)
→ abc (Using C → c)
Derivation-03:
S → ABC
→ AbC (Using B → b)
→ Abc (Using C → c)
→ abc (Using A → a)
The other 2 derivations are leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation.
Point-05:
- Leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation of a string may be exactly same.
- In fact, there may exist a grammar in which leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation is exactly same for all the strings.
Example
Consider the following grammar-
S → aS / ∈
The language generated by this grammar is-
L = { an , n>=0 } or a*
All the strings generated from this grammar have their leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation exactly same.
Let us consider a string w = aaa.
Leftmost Derivation-
S → aS
→ aaS (Using S → aS)
→ aaaS (Using S → aS)
→ aaa∈
→ aaa
Rightmost Derivation-
S → aS
→ aaS (Using S → aS)
→ aaaS (Using S → aS)
→ aaa∈
→ aaa
Clearly,
Leftmost derivation = Rightmost derivation
Similar is the case for all other strings.
Point-06:
- For a given parse tree, we may have its leftmost derivation exactly same as rightmost derivation.
Point-07:
- If for all the strings of a grammar, leftmost derivation is exactly same as rightmost derivation, then that grammar may be ambiguous or unambiguous.
Example
Consider the following grammar-
S → aS / ∈
- This is an example of an unambiguous grammar.
- Here, each string have its leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation exactly same.
Now, consider the following grammar-
S → aS / a / ∈
- This is an example of ambiguous grammar.
- Here also, each string have its leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation exactly same.
Consider a string w = a.
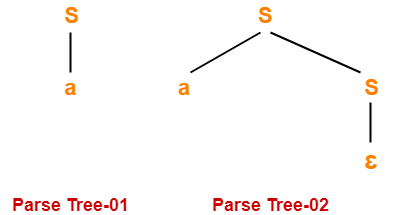
Since two different parse trees exist, so grammar is ambiguous.
Leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation for parse tree-01 are-
S → a
Leftmost derivation and rightmost derivation for parse tree-02 are-
S → aS
S → a∈
S → a
Next Article- Language of Grammar
Get more notes and other study material of Theory of Automata and Computation.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.
Summary

Article Name
Ambiguous Grammar | Parse Tree | Important Points
Description
Important Points about Ambiguous Grammar and Parse Tree- Ambiguous grammar is a grammar whose all strings have exactly one parse tree. Parse tree is a geometrical representation of a derivation.
Author
Akshay Singhal
Publisher Name
Gate Vidyalay
Publisher Logo

Source: https://www.gatevidyalay.com/ambiguous-grammar-parse-tree-important-points/
0 Response to "How to Draw Parse Tree for Given Grammer"
Publicar un comentario